
Total Knee Replacement Surgery

Knee Replacement Surgery

Knee Replacement Surgery

Knee Replacement Surgery

Knee Replacement Surgery
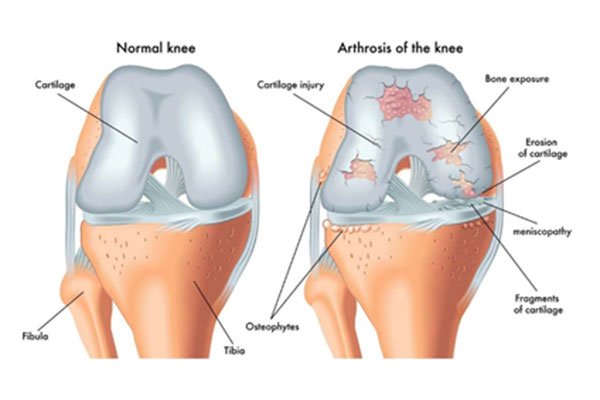
The knee is made up of the femur (thigh bone), the tibia (shin bone), and patella (kneecap). The meniscus, the soft cartilage between the femur and tibia, serves as a cushion and helps absorb shock during motion.
Arthritis (inflammation of the joints), injury, or other diseases of the joint can damage this protective layer of cartilage, causing extreme pain and difficulty in performing daily activities. We may recommend surgery if non-surgical treatment options have failed to relieve the symptoms.
Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial parts.
Total knee replacement surgery is commonly indicated for severe osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis is the most common form of knee arthritis in which the joint cartilage gradually wears away. It often affects older people.

We may advise total knee replacement if you have:
- Severe knee pain which limits your daily activities (such as walking, getting up from a chair or climbing stairs).
- Moderate to severe pain that occurs during rest or awakens you at night.
- Chronic knee inflammation and swelling that is not relieved with rest or medications.
- Failure to obtain pain relief from medications, injections, physical therapy, or other conservative treatments.
- knee deformity
Causes
The exact cause of osteoarthritis is not known, however there are a number of factors that are commonly associated with the onset of arthritis and may include:
- Injury or trauma to the joint.
- Fractures at the knee joint.
- Increased body weight.
- Repetitive overuse.
- Joint infection.
- Inflammation of the joint.
- Connective tissue disorders.
Diagnosis
We will diagnose osteoarthritis based on the medical history, physical examination, and X-rays.
X-rays typically show a narrowing of joint space in the arthritic knee.
Management
You can relieve OA at home. First, get enough rest. You can try anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, Diclofenac or Naproxen. They can provide fast relief for mild to moderate arthritis pain.
Viscosupplementation Hyaluronic acid injected into an arthritic joint can afford symptomatic relief of pain and stiffness in about 70% of cases. The injections can be repeated up to 3 times for maximal effect.
- Losing weight reduces pain and stiffness.
- Exercise helps joints work better.
- Without treatment, OA usually gets worse.
- Joint replacement gets rid of pain.
- Rehabilitation is vital after joint replacement surgery.
What medications should I stop before operation?
- Many tablets can cause excessive bleeding at operation so it is essential to cease taking the medication well beforehand. However, if you are taking such medication for problems with your heart or blood vessels, please ensure you discuss this us.
- Clopidogrel, Warfarin/Coumarin/Marevan cease 5 days pre-op.
Reasons that you may benefit from Total Knee Replacement commonly include.
- You will be easily able to do your everyday activities, including walking, going up and down stairs, and getting in and out of chairs.
- No pain while resting, either day or night.
- Deformity of knee is corrected.
- No need to take pain killers further.
Most patients who undergo Total Knee Replacement are aged 60 to 80, but we evaluate patients individually. Recommendations for surgery are based on a patient’s pain and disability, not necessarily age.
We have patients as young as age 20 and older than 95 who have undergone successful Total Knee Replacement.
Preparing For Surgery
If you decide to have Total Knee Replacement surgery, we may organise for you to see one of our cardiovascular physicians, with whom we work, for a complete medical assessment and to optimize your fitness for the operation. This is especially likely if you have a strong history of DVT, serious cardiac disease or are on anticoagulants or other blood thinners.
Other Investigations includes routine blood tests, urine analysis, 2d-echo, ECG and X-rays including a chest X-ray.
Your stay in hospital
Patient stay at our hospital is around 1-2 days.
We allow immediate weight bearing on 2nd post op day and stair climbing before discharge.
Foot and ankle movement is encouraged immediately following surgery to also increase blood flow in your leg muscles to help prevent leg swelling and blood clots. Most patients begin exercising their knee the day after surgery. Our physiotherapists will teach you specific exercises to strengthen your leg and restore knee movement to allow walking and other normal daily activities soon after your surgery particularly concentrating on getting the knee fully straight and flat by quadriceps contraction. Bending is encouraged but not forced, and always comes once the swelling goes down. This may take 6 weeks or more.
Risks & Complications
As with any major surgery, possible risks and complications associated with total knee replacement surgery include:
- Knee stiffness
- Infection
- Blood clots (deep vein thrombosis).
- Nerve and blood vessel damage.
- Ligament injuries
- Patella (kneecap) dislocation
- Plastic liner wears out
- Loosening of the implant
Avoiding Problems After Surgery
Blood clot prevention: Follow our instructions carefully to minimize the potential of blood clots that can occur during the first several weeks of your recovery.
Warning signs of possible blood clots in your leg include:
- Increasing pain in your calf.
- Tenderness or redness above or below your knee.
- Increasing swelling in your calf, ankle, and foot.
Warning signs that a blood clot has travelled to your lung include:
- Sudden increased shortness of breath.
- Sudden onset of chest pain.
- Localised chest pain with coughing.
Notify your us immediately if you develop any of these signs.
Warning signs of a possible knee replacement infection are:
- Persistent fever (higher than 100 degrees orally).
- Shaking chills.
- Increasing redness, tenderness, or swelling of the knee wound.
- Drainage from the knee wound.
- Increasing knee pain with both activity and rest.
Notify your us immediately if you develop any of these signs.
Some physiotherapy exercises post surgery are like

Knee bending high sitting

Straight leg raise

Knee quadriceps extensor
How your New Knee is different?
You may feel some numbness in the skin around your incision. You also may feel some stiffness, particularly with excessive bending activities. Improvement of knee motion is a goal of total knee replacement.
The motion of your knee replacement after surgery is predicted by the motion of your knee prior to surgery. Most patients can expect to nearly fully straighten the replaced knee and to bend the knee sufficiently to go up and down stairs and get in and out of a car.
Occasionally, you may feel some soft clicking of the metal and plastic with knee bending or walking. These differences often diminish with time and most patients find these are minor, compared to the pain and limited function they experience prior to surgery.
Your new knee may activate metal detectors required for security in airports and some buildings. Tell the security agent about your knee replacement if the alarm is activated.
So, If you find difficulty in performing simple activities such as walking or climbing stairs because of your severe arthritic knee pain, then total knee replacement may be an option for you. It is a safe and effective procedure to relieve pain, correct leg deformity, and help you resume your normal activities of daily living.
